
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部 保育。保護。享受。
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部  目錄
目錄潮汐沼澤森林和森林
該群組包括沿海平原內部河流及其支流上潮,以及弗吉尼亞州東南部的風潮河口上部受到潮汐洪的地區發生的所有森林和森林地。河口系統的森林植被發展和持久性似乎受到鹽度限制下游,而上游受到足夠的沉澱物供應量所限制。
Tidal hardwood swamps occur along all of the major eastern Virginia rivers from the James River northward, but are most extensively developed along the Pamunkey and Mattaponi Rivers, where regular tidal inundation is unimpeded by levees or channel alteration. Its habitats are influenced by lunar tides up to 1 m (3 ft), but diluting freshwater flows from upstream keep salinity levels below 0.5 ppt. Communities in this group are structurally complex, with semi-open overstories and diverse multiple lower strata. Pumpkin ash (Fraxinus profunda) and swamp tupelo (Nyssa biflora) are the most abundant overstory species, with occasional associates of red maple (Acer rubrum), green ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica), sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua), swamp chestnut oak (Quercus michauxii), common persimmon (Diospyros virginiana), and black gum (Nyssa sylvatica). From the Potomac River north, green ash becomes increasingly important and largely replaces pumpkin ash as an overstory dominant in northern Virginia. Shrub layers are mixed and extraordinarily diverse. Common species include winterberry (Ilex verticillata), smooth alder (Alnus serrulata), southern wild raisin (Viburnum nudum), arrow-wood (Viburnum dentatum), wax myrtle (Morella cerifera), American holly (Ilex opaca var. opaca), fetterbush (Eubotrys racemosus), spicebush (Lindera benzoin var. benzoin and var. pubescens), sweetbay magnolia (Magnolia virginiana var. virginiana), swamp rose (Rosa palustris), silky dogwood (Cornus amomum) stiff dogwood (Cornus foemina) , and Virginia-willow (Itea virginica). Climbing vines such as poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans var. radicans), Virginia-creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia), and greenbriers (Smilax spp.) are also common. Herb layers are rich with a wide variety of wetland ferns, graminoids, and forbs. Characteristic herbs are halberd-leaf tearthumb (Persicaria arifolia), groundnut (Apios americana), rice cutgrass (Leersia oryzoides), arrow-arum (Peltandra virginica), false nettle (Boehmeria cylindrica), water-hemlock (Cicuta maculata var. maculata), Virginia dayflower (Commelina virginica), lizard's-tail (Saururus cernuus), fringed sedge (Carex crinita), orange jewelweed (Impatiens capensis), Canada mint (Mentha canadensis ), royal fern (Osmunda spectabilis), cowbane (Oxypolis rigidior), and greater marsh St. John's-wort (Triadenum walteri). Stands transitional between more closed forest and open marsh may contain abundant wild rice (Zizania aquatica var. aquatica).
潮汐硬木沼澤棲息地的一個有影響力,是明顯的凹凸顯微地形,高於最高潮水平以上的地形提供穩定的基礎,可以為樹木建立更多中生物植物的微生境。這些沼澤森林還支持神秘的動物種,例如(Pro tonataria citrea)和雙腳(Amphiuma 意思),以及更明顯的物種,包括白鷹(H aliaee atus leucocephalus)。潮汐硬木沼澤被認為全球罕見到稀有,並受到侵入性的沼澤(Murdannia keisak)、長期海平面上升和昆蟲病原體的威脅。幾十年來,冠部死亡和樹木死亡已成為這些社區幾乎無處不在的現象,一般來說是由於海平面上升和鹽度漸變的上游變化。然而,在過去十年中,引入的祖母綠白山灰鷹的爆發導致了許多樹木中主要的白蠟樹死亡。在某些地方,樹木密度如此低,以至於淡水沼澤植被正在恢復棲息地。

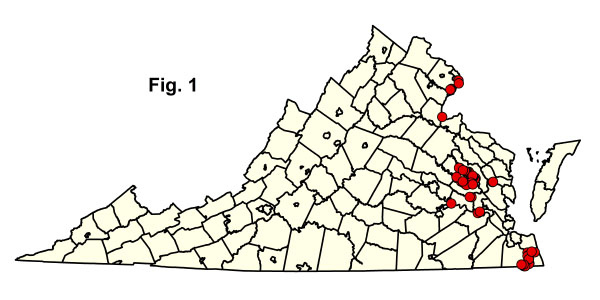
針葉草(Taxodium distichum)主導的針葉樹林或混合沼澤森林和森林,僅從馬里蘭州、弗吉尼亞州東南部和北卡羅來納州的河流上潮流中知道。弗吉尼亞州記錄了月潮龍沼澤/皮安卡坦克河(格洛斯特,國王和皇后和米德爾塞克斯縣),奇卡霍米尼河(查爾斯市,詹姆斯城和新肯特縣)和詹姆斯河(懷特島和薩里縣);以及風潮潮西北和北陸河(切薩皮克市和弗吉尼亞海灘)。在某些地點,這些社區出現在潮汐沼澤和非潮汐後沼澤或高原之間的生態區。
在月潮中,白柏樹( Taxodium distichum )主導著開放到非常開放的覆蓋層,有或沒有硬木相關聯物,例如沼澤花( Nyssa biflora),水龍(Nyssa aquatica)和綠灰(Frax inus pennsylvanica)。樹木結構和樹冠覆蓋範圍從封閉森林到非常開放的森林。灌木和草本層是不同的,但通常包含沼澤和沼澤特徵的物種混合物種。一些發展良好的潮汐白柏樹森林看起來像海豚的白羊皮-圖佩洛沼澤相似。其他樹木具有近單特性的草本主導地位於海岸稻草(Carex hyalinolepis)。在西北河上的一個獨特,可能受到火影響的草原狀植物,主要的草本植物,按季節嚴峻的順序排列,是銀色的稻草(Carex canescens var.不同的)、尖 刺(艾洛哈里斯·羅斯特拉 塔)、鈴蛇大師(Eryn gium aquaticum)和野稻(Zizania aqu atica var. 水族) 。
A distinctive, mixed tidal swamp forest in extreme southeastern Virginia is subject to irregular wind-tidal flooding. As currently defined, this community type appears to be a globally rare endemic of the Embayed Region of southeastern Virginia and northeastern North Carolina; similar communities, however, occur occasionally further north on the irregularly flooded edges of lunar-tidal systems. In Virginia, stands occur primarily along the North Landing and Northwest Rivers (Cities of Virginia Beach and Chesapeake), estuarine tributaries of Currituck Sound. Although these systems are no longer influenced by lunar tides because of inlet closures, they are subject to wind-driven currents that produce as much as 1 m (3 ft) of variation in water levels and contribute to a salinity regime that fluctuates between completely fresh and about 5 ppt. This forest borders the wind-tidal marshes along the lower portions of the two rivers, extending well upstream of the limit of marshes in narrowing channel-side belts. It appears to represent a long-term seral stage in succession from marsh to swamp forest. Habitats have a pronounced hummock-and-hollow microtopography, with an average flooding depth 40 cm (16 in) above the hollow bottoms. Soils are coarse, fibric peats that appear indistinguishable from adjacent marsh peats. Swamp tupelo (Nyssa biflora), bald cypress (Taxodium distichum), and loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) are the dominant overstory trees in variable combinations. Spanish-moss (Tillandsia usneoides) is locally abundant, festooning the trees in some stands. Sweetbay magnolia (Magnolia virginiana var. virginiana) and red bay (Persea palustris) are scattered understory trees, while wax myrtle (Morella cerifera) dominates the shrub layer. The herb layer is diverse, containing species characteristic of both marshes and swamps, but royal fern (Osmunda spectabilis) often dominates.
潮汐白柏樹森林和林地的環境動態,組成變化和全州的分佈局尚不清楚,需要密集研究。
參考:阿納特(1960),庫林(2002),杜姆萊爾等。(1985),弗萊明和穆爾黑德(1998),麥科伊和弗萊明(2000),萊因哈特(1992)。
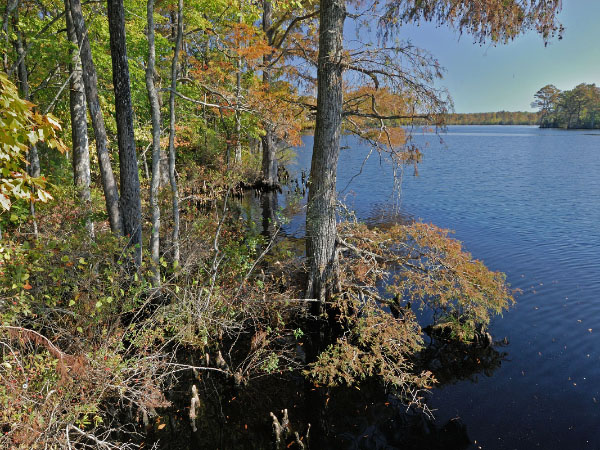 © DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
© DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
 下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。
下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。 
