
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部 保育。保護。享受。
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部  目錄
目錄海上沼澤
該群組包括所有季節性洪水的木質植被,以及受保護和近河口的海洋濕地的飽和森林。在海洋棲息地中,單一植物類型的植物生理學可能會因繼續發育階段以及受風和鹽霧的修剪的程度而有很大的變化。因此,相同的植被類型可以表示為不同條件下不同地點的灌木、森林或森林。一個很好的例子是黑柳(Salix nigra)類型的海上沼澤森林,它最初可能成為灌木地,但隨著樹木成長時,很快就會獲得森林或森林身長。儘管如此,這個群組通常可以分為海上灌木沼澤和海上沼澤森林,不僅通過其成熟的生理學,還可以按花卉成分組成。
海上灌木沼澤是季節性洪水,通常是密集的灌木叢,包括遮蔽的背沙丘凹陷和入口頭,地面水在一年中大部分都存在。水文學的特徵是坐落的水平和間歇性到季節性的洪水。地下水和地面水通常都是淡水(< 0。5 ppt),儘管在颱風等事件期間的暴風暴浪之後,鹽水可能會在這些地區積聚。土壤分層,在濕沙上,厚度高達 30 厘米(12 英寸)的薄泥層。這些社群的物種組成很多變化,並且從東南海岸(弗吉尼亞海灘市)到東岸(阿科馬克和北安普頓縣)有些變化。在整個地區,蠟菊(Morella cerifera)是特徵主導地位。南部地區具有墨水果( Ilex glabra )和高灌木藍莓(Vaccinium spp.)。這些物種在東岸北部的這個群體中不太重要。有毒常春藤的攀爬葡萄藤(毒桿菌株)var.在這些沼澤的大多數情況下,根植物)與灌木充分相交織。草本層可能含有豐富的植物植物,包括皇家楊桃( Osmunda spectabilis),沼澤植物( Thelypteris palustris var. 青春菊)、網狀 鏈上植物 ( 洛林西里亞) 和維吉尼亞連鎖杉樹 ( Woodwardia virginica),但也包括各種植物,例如螺旋草 (Hydrocotyle verticillata)。海上灌木沼澤的分類、地理分佈和保育狀況目前有些不確定,需要密集研究。
Maritime swamp forests are seasonally flooded and saturated forests occupying large, protected, interdune swales, flats immediately behind tidal marshes, and the bottoms of streams just inland from estuarine zones. These communities definitely occur from southern New Jersey to North Carolina, but may range further south. In Virginia, stands are scattered along the outer Coastal Plain from the Eastern Shore (Accomack and Northampton Counties) to Cape Henry and False Cape (City of Virginia Beach). The status of these communities on the western shore of the Chesapeake Bay is less clear. Habitats are generally characterized by hummock-and-hollow microtopography, with mucky to sandy, mottled soils and sizeable areas of seasonally standing water. The apparent nutrient status and flooding regimes of soils are highly variable and probably relate to the wide compositional variation in documented stands. Dominant overstory trees in the seasonally flooded forests of the group include red maple (Acer rubrum), sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua), swamp tupelo (Nyssa biflora), blackgum (Nyssa sylvatica), black willow (Salix nigra), sweetbay magnolia (Magnolia virginiana var. virginiana) and, less frequently, bald cypress (Taxodium distichum) and Atlantic white-cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides). Shrubs are diverse but usually include highbush blueberries (Vaccinium fuscatum and/or Vaccinium formosum), wax myrtle (Morella cerifera), red bay (Persea palustris), and greenbriers (Smilax spp.). Herb layers range from floristically depauperate, with dominance by Virginia chain fern (Woodwardia virginica) or low shrubs, to species-rich with a diversity of marsh and swamp species.
Saturated pine forests in this group occur in back-dune depressions of barrier islands and on terrace flats bordering estuaries further inland. In Virginia, these communities are locally scattered along the Chesapeake Bay (both shores) and its major estuarine tributaries, as well as around Back Bay and estuarine tributaries of Currituck Sound in the southeastern corner of the state. Occasionally, stands occupy slightly elevated "islands" within the upper portions of salt marshes. Habitats are level flats with shallow water tables and hummock-and-hollow microtopography. Areas of seasonally ponded water and organic muck are present; elsewhere, soils are heavily mottled sands. Loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) is the usual dominant overstory tree, sometimes with hardwood associates. Wax myrtle (Morella cerifera) and vines of common greenbrier (Smilax rotundifolia) and poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans var. radicans) are usually abundant. In southern areas (e.g., on False Cape), pond pine (Pinus serotina) and inkberry (Ilex glabra) are characteristic woody associates. Wetland species such as cinnamon fern (Osmundastrum cinnamomeum), royal fern (Osmunda spectabilis), switchgrass (Panicum virgatum var. virgatum and var. cubense), and smartweeds (Persicaria spp.) dominate species-poor herb layers. A distinctive variant occurring in southeastern Virginia and North Carolina has a dense understory of switch cane (Arundinaria tecta). Some of the maritime wet pine forests appear to represent formerly open, bog-like maritime grasslands that have been invaded by loblolly pines. There is a well documented example of this variant from the Eastern Shore (Assateague Island, Accomack County) and at least one poorly documented occurrence on False Cape (City of Virginia Beach). These stands occupy swales in sheltered back dunes that are protected from salt spray except during major storm surges. A thin organic layer, frequently covered by dense mats of Sphagnum mosses, is usually present at the soil surface. On Assateague Island the vegetation is an open stand of young, salt-spray-stunted loblolly pine, with a very sparse shrub layer. Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) forms dense mats locally beneath the pines. Elsewhere, scattered herbs include saltmeadow cordgrass (Spartina patens), tall flat panic grass (Coleataenia rigidula ssp. rigidula), and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum var. virgatum) in shallow pools and depressions, and bushy bluestem (Andropogon glomeratus), Virginia marsh St. John's-wort (Triadenum virginicum), beaksedges (Rhynchospora spp.), twisted yellow-eyed grass (Xyris torta), white-bracted thoroughwort (Eupatorium leucolepis), and water sundew (Drosera intermedia) in wet sand and Sphagnum mats. Maritime Wet Pine Forests are similar to and often intergrade with non-wetland maritime loblolly pine forests and maritime evergreen forests.
海上沼澤的生態動態,以及它們與內陸沼澤森林的區別,尚不了解。與海洋區的其他社區一樣,它們會受到風暴浪、鹽霧和沙丘移動的潛在干擾。海洋沼澤森林在弗吉尼亞州非常罕見,並且可能受到侵入的發展、開採和農業污染物。
參考文獻:哈維爾(1967),弗萊明和穆爾黑德(1998),自然保護局(1997)。
 © DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
© DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
代表性社區類型:
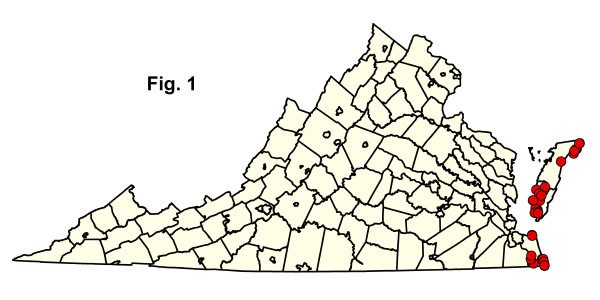
數據是從位於三個海岸平原縣的 33 海上沼澤地圖收集的(圖 1)。1)。這些樣本大多數都是森林沼澤,需要來自灌木沼的其他數據。弗吉尼亞州海洋植物數據的分析雖然有些有限,但似乎足夠來描述弗吉尼亞類型的組成以及它們與 USNVC 的關係。從切薩皮克灣西岸對此群體的社區記錄仍然是首要任務。點擊下面的任何突出顯示的 CEGL 代碼以查看由 NatureReserve 瀏覽器提供的全球 USNVC 描述。
 下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。
下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。

