
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部 保育。保護。享受。
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部  目錄
目錄北部紅橡樹林
Dominance by northern red oak (Quercus rubra) characterizes these forests, which reach maximal importance at elevations above 900 m (3,000 ft) throughout western Virginia. Similar forests are found throughout higher elevations of the Southern and Central Appalachians. Although composition varies with parent material and landscape position, prolonged weathering and limited accumulation of soil organic matter have generally resulted in moderately to strongly infertile soils and consequently moderate to low species richness. In addition to the prevalent red oaks, scattered associates of white oak (Quercus alba), birches (Betula alleghaniensis and Betula lenta), and black cherry (Prunus serotina var. serotina) are often present in the overstory. Typical small trees and shrubs include mountain holly (Ilex montana), witch-hazel (Hamamelis virginiana), striped maple (Acer pensylvanicum), minnie-bush (Menziesia pilosa), early azalea (Rhododendron prinophyllum), beaked hazelnut (Corylus cornuta var. cornuta), and sprouts of American chestnut (Castanea dentata). In southwestern Virginia stands with Southern Appalachian affinities, flame azalea (Rhododendron calendulaceum), southern mountain cranberry (Vaccinium erythrocarpum), and mountain highbush blueberry (Vaccinium simulatum) are characteristic shrubs. Stands typically contain ground layers of hayscented fern (Dennstaedtia punctilobula), New York fern (Parathelypteris noveboracensis), low ericaceous shrubs (e.g., lowbush blueberry, [Vaccinium pallidum]), or patches of graminoids such as Pennsylvania sedge (Carex pensylvanica) and wavy hairgrass (Avenella flexuosa). Other characteristic herbs include fly-poison (Amianthium muscitoxicum), poke milkweed (Asclepias exaltata), panicled hawkweed (Hieracium paniculatum), whorled loosestrife (Lysimachia quadrifolia), eastern lousewort (Pedicularis canadensis), rattlesnake-roots (Prenanthes spp.), whorled aster (Oclemena acuminata), cut-leaved goldenrod (Solidago arguta var. arguta), and Curtis' goldenrod (Solidago curtisii).
此群中的大部分樹木曾經由美國栗子(Castanea dentata)主導或共同主導,然後在 20 世紀初被引入的真菌病(Cryphonectria parasitica)破壞,除了最無法訪問的樹木之外,所有除了最無法訪問的樹木之前都被挖掘和/或放牧。較多暴露的地方的樹木通常表現短暫且有彎曲的身材,反映了大風和頻繁的冰傷的影響。高海拔處置前的栗子和混合橡木栗林,可能會經歷一次 40-60 年一次由閃電擊發生的低強度火災。當代的火災排除,以及地底層中有多種競爭的植物,導致橡樹再生不良,並在許多山上紅橡樹林中受到紅楓( Acer rubrum )或紅楓( Acer saccharum )等間生物植物侵入。吉普賽蟲侵襲,導致藍嶺北部重複脫葉和廣泛的樹木死亡,是對這個和其他橡木主導的社區的另一種嚴重威脅。
參考文獻:阿布拉姆斯等。( 1997 )、Agrawal 和 Stephenson( 1995 )、Coulling 和 Rawinski( 1999 )、Fleming 和 Coulling( 2001 )、Johnson 和 Ware( 1982 )、Rawinski等人。( 1994 ),Rawinski等人。( 1996 )、Rheinhardt 和 Ware( 1984 )、Stephenson( 1982 a)、Stephenson( 1982 b)、Stephenson 和 Adams( 1989 )、Stephenson 和 Adams( 1991 )。
 © DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
© DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
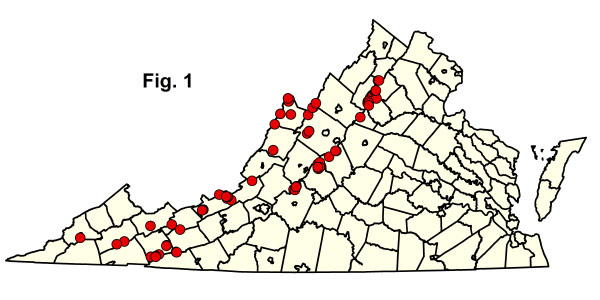
北部紅橡樹森林通過來自西弗吉尼亞州 26 縣的 86 土地樣本記錄得了相當良好的記錄(圖。1)。常綠灌木類型(見下文)是弗吉尼亞州相對罕見的社區,需要額外的清查和採樣。點擊下面的任何突出顯示的 CEGL 代碼以查看由 NatureReserve 瀏覽器提供的全球 USNVC 描述。
 下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。
下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。

