
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部 保育。保護。享受。
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部  目錄
目錄基本橡木-山核桃森林
弗吉尼亞州基本橡木-胡科里森林的主要棲息地是從地下到地下高地,而基本的火山和變形岩石,例如糖尿布,石灰岩,雙酚和元石(綠石)。土壤範圍從中酸度到環中性,含有適度高的鈣,鎂,錳,鐵和鋁。DCR-DNH 生態學家使用的「鹼性」一詞指的是高水平的鹼陽離子飽和度,而不是土壤 pH 值,後者的分析已被證明是肥力和母質的不太可靠的指標。這群組中的社區分散在維吉尼亞皮埃蒙特各地,以及北部藍嶺的較低高度斜坡上;內部沿岸平原肥沃地帶上非常少量的樹木也被記錄。這種植被最大的斑點發生在皮埃蒙特三世紀流域;在皮埃蒙特島其他地方更廣泛的馬菲和超大地形構造的侵入;以及藍山嶺和其山腳中的元岩石(綠石)衍生的土壤上。

Overstory composition varies regionally, but is generally characterized by mixtures of white oak (Quercus alba), northern red oak (Quercus rubra), black oak (Quercus velutina), chestnut oak (Quercus montana), post oak (Quercus stellata), pignut hickory (Carya glabra), red hickory (Carya ovalis), shagbark hickory (Carya ovata), mockernut hickory (Carya tomentosa), white ash (Fraxinus americana), and tulip-tree (Liriodendron tulipifera). Hickories are especially abundant in these forests and may dominate some stands. Dominance by tulip-tree usually follows heavy logging or other catastrophic disturbances. Eastern redbud (Cercis canadensis var. canadensis), eastern hop-hornbeam (Ostrya virginiana), and flowering dogwood (Cornus florida) are common understory species. Herb layers are typically patchy but species-rich and support diverse mixtures of both mesophytic and dry-site species. In the spring, small geophytes such as cut-leaf toothwort (Cardamine concatenata), rue-anemone (Thalictrum thalictroides), star chickweed (Stellaria pubera), and spring beauty (Claytonia virginica var. virginica) frequently carpet the ground layers of these oak-hickory forests. The summer and fall aspect is dominated by forbs and grasses such as woodland agrimony (Agrimonia rostellata), four-leaf milkweed (Asclepias quadrifolia), curlyheads (Clematis ochroleuca), Bosc's panic grass (Dichanthelium boscii), naked-flowered tick-trefoil (Hylodesmum nudiflorum), bottlebrush grass (Elymus hystrix), bedstraws (particularly Galium circaezans and Galium latifolium), eastern solomon's-plume (Maianthemum racemosum ssp. racemosum), rock muhly (Muhlenbergia sobolifera), goldenrods (particularly Solidago caesia var. caesia and Solidago ulmifolia), yellow pimpernel (Taenidia integerrima), lesser horse-gentian (Triosteum angustifolium), and wood violet (Viola palmata var. triloba).
基本橡木-胡桃樹林佔用了更多肥沃的土壤,具有更高的物種豐富,並且具有較少的螺紋灌木叢和酸性橡木森林。它們與山山橡樹木樹林區別於其限制在低海拔棲息地,以及相應的組成,主要由不出現在高處的物種組成。由於皮埃蒙特地區的分佈局已經受到有限的可用棲息地限制,基本橡樹木森林也因長期的農業歷史,硬木森林轉換為密集管的松樹木樹木以及城市發展而大幅減少。目前,在許多這樣的社區中,橡樹的生長情況不佳,而白蠟樹中通常占主導地位的成分正受到昆蟲病原體翡翠灰螟的侵襲。此群組中的一些社區類型可以被認為在該州中不常見或罕見。
參考文獻:法雷爾和韋爾(1991),弗萊明(2002 a),弗萊明(2002 b),弗萊明和庫林(2001),弗萊明和帕特森(2004),弗萊明和韋伯(2003),韋爾(1991),韋爾(1992)。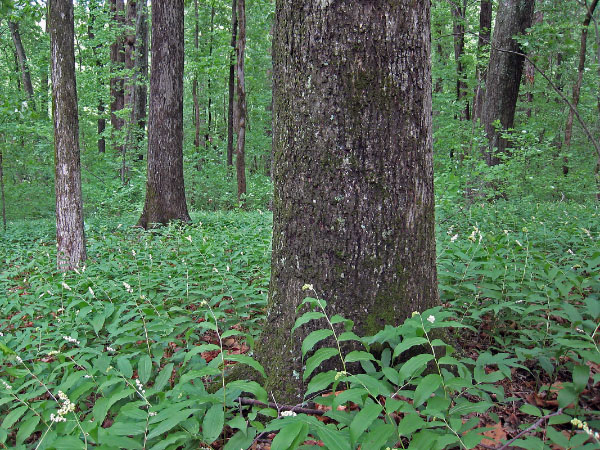 © DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
© DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
這個生態組通過定量數據非常好地表現,它的分割為社區類型得到 151 繪圖樣本的區域分析支持(圖。1)。基本橡樹木森林包括弗吉尼亞州一些最富有物種的植物,並且已定義的單位主要由地理和細微的花卉差異分隔開,這些植物在田野上可能難以區分。單擊下面的任何突出顯示的 CEGL 代碼以查看 NatureServe Explorer 提供的全球 USNVC 描述 下載以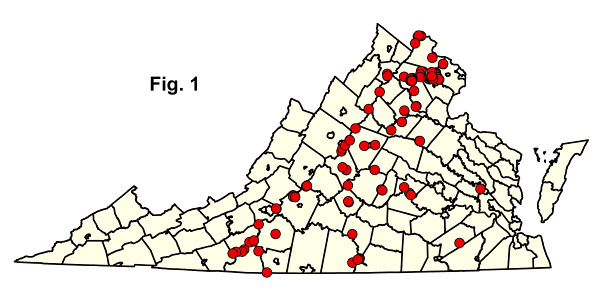
 下列出的每種社區類型的組成摘要統 計表。
下列出的每種社區類型的組成摘要統 計表。

