
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部 保育。保護。享受。
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部  目錄
目錄池塘松樹林和波科辛
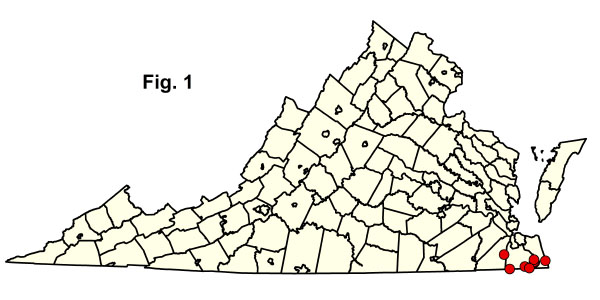
This ecological group is characterized by coniferous, pyrophytic woodlands of saturated, oligotrophic, Coastal Plain peatlands. These communities are restricted to southeastern Virginia, eastern North Carolina, and northeastern South Carolina. Although no doubt more widespread in the pre-settlement Virginia landscape, only a few remnants of these communities are currently found in the extreme southeastern part of the state. The largest extant occurrences are in the Great Dismal Swamp National Wildlife Refuge (Cities of Suffolk and Chesapeake) and on remote peat flats beyond the range of wind-tidal flooding along the North Landing River (City of Virginia Beach) and Northwest River (City of Chesapeake). Pond Pine Woodlands and Pocosins have high biomass and consist largely of inflammable woody plants that are specially adapted to frequent, intense burning. All present-day examples in Virginia suffer to some extent from a reduction in fire frequencies or complete suppression of fires. Stand physiognomy and composition reflect responses to gradients of fire frequency and peat depth. Stands known as "high pocosins" are associated with deeper organic soils and more frequent fires; these have only scattered, stunted pond pines (Pinus serotina) emergent from nearly impenetrable evergreen shrub thickets dominated by shining fetterbush (Lyonia lucida), inkberry (Ilex glabra), Carolina laurel (Kalmia carolina), and laurel-leaf greenbrier (Smilax laurifolia). Stands associated with superficial peat and/or longer periods without fire often develop nearly closed canopies of larger pond pines, understories of red maple (Acer rubrum), sweetbay magnolia (Magnolia virginiana var. virginiana), and red bay (Persea palustris), and less dense shrub layers that contain more deciduous species. Few herbaceous species except Virginia chain fern (Anchistea virginica) thrive in pond pine woodlands.
池塘松樹林在密集的甘蔗(Arundinaria tecta)(Arundinaria tecta)上,被稱為 " Canebrakes," 曾經常常見於惡劣沼澤地區的回火間隔非常短。由於排除火災,這些森林連續被非河流森林取代,儘管電力線仍然存在非天然類似物質,通過割草和除草劑維護的通道權。
池塘松樹林和波科辛的花卉上與泥灘大西洋白雪松森林和混合常綠類型的非河流沼澤森林相似。它們與前者不同,在過層的主導地位,灌木密度更大,以及與以前的泥炭地相關性,這些土壤之間的火焰回報間隔得多少。非河流沼澤森林(混合常青樹型)擁有更多樣化的樹冠,在沙丘或古沙丘地區佔地較潮濕,並且可能因泥炭深度和火災頻率而有所不同。由於碎片和沒有持續火頻率,這個群體在全球範圍內非常罕見,迅速下降,並且幾乎無可生存。
參考文獻:院長(1969),福卡齊奧等。(1998),弗萊明和穆爾黑德(1998),弗羅斯特(1995),史蒂文斯和帕特森(1998)。
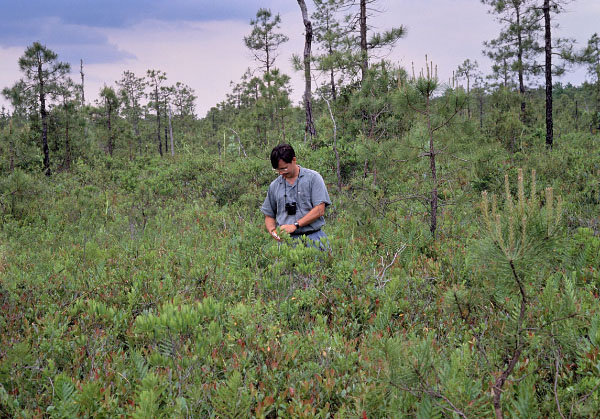 © DCR-DNH,托馬斯·J·拉溫斯基。
© DCR-DNH,托馬斯·J·拉溫斯基。
 下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。
下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。

