
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部 保育。保護。享受。
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部  目錄
目錄酸性橡木-山核桃森林
Forests in this group are similar to those of the Basic Oak-Hickory Forests, but occupy submesic to subxeric upland sites with soils weathered from subacidic parent material such as siltstone, metasiltstone, shale, certain granites, and various metamorphic rocks. These forests are widely distributed throughout the Piedmont, mountain valleys, and lower mountain slopes of both the Blue Ridge and Ridge and Valley, up to about 600 m (2,000 ft) elevation. They were probably once also frequent in better soils of the Coastal Plain, but now only widely scattered remnants remain there. Hickories (Carya spp.) are less abundant than in the Basic Oak-Hickory Forests group but are nevertheless common, often primarily as understory trees. Dominant oaks include white oak (Quercus alba), black oak (Quercus velutina), scarlet oak (Quercus coccinea), northern red oak (Quercus rubra), southern red oak (Quercus falcata), and chestnut oak (Quercus montana). Flowering dogwood (Cornus florida) is a characteristic, often abundant understory tree, although its numbers have been greatly reduced in recent decades by the fungal pathogen dogwood anthracnose (Discula destructiva). Deciduous ericads, especially lowbush blueberry (Vaccinium pallidum) and deerberry (Vaccinium stamineum), are usually present but patchy in the shrub layer, along with maple-leaved viburnum (Viburnum acerifolium). Herbaceous diversity is somewhat less than in Basic Oak-Hickory Forests but considerably greater than in Oak/Heath Forests. Typical herbs of these communities include plaintain-leaved pussytoes (Antennaria plantaginifolia), Pennsylvania sedge (Carex pensylvanica), whorled coreopsis (Coreopsis verticillata), poverty oatgrass (Danthonia spicata), common dittany (Cunila origanoides), rattlesnake weed (Hieracium venosum), large summer bluets (Houstonia purpurea), low St. Andrew's cross (Hypericum stragulum), whorled loosestrife (Lysimachia quadrifolia), violet woodsorrel (Oxalis violacea), gray beard-tongue (Penstemon canescens), solomon's-seal (Polygonatum biflorum var. biflorum), lion's foot (Nabalus serpentarius), wild pink (Silene caroliniana var. pensylvanica), silverrod (Solidago bicolor), wavy-leaved aster (Symphyotrichum undulatum), and wood vetch (Vicia caroliniana).
酸性橡木果樹林是種類豐富的基礎橡木果樹林和花卉去角質橡樹林之間的生態中間體中間體。它們佔用了肥沃的土壤較少,物種豐富性較低,並且具有更多生長的灌木叢和基本橡木森林。它們與山山橡木-胡桃樹林區分別於其限制在低海拔或地下棲息地,以及相應的組成,主要由不出現在高處的物種組成。有許多當代酸橡木森林的樹木樹林都受到火災排除的影響,包括橡木招募不良,以及紅楓( Acer rubrum )、美國山毛毛 (Fagus grandifolia) 和黑膠(Nyssa sylvatica)等不耐火的間生物種侵入了地下。
參考文獻:弗萊明(2002 b),弗萊明(2007),弗萊明和庫林(2001),弗萊明和穆爾黑德(2000),弗萊明和帕特森(2004),格姆博里斯(1974),奧爾森和胡普(1986)。 © DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
© DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
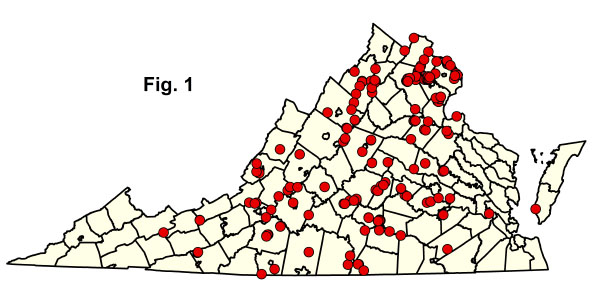
 下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。
下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。

