
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部 保育。保護。享受。
 保育與休閒部
保育與休閒部  目錄
目錄山脈乾燥和乾燥的梅西克鈣森林
該群主要涵蓋山脈混合硬木森林,其中重要成分為橡樹,並發生在石灰岩、土石,以及較少頻繁地的岩石、泥石和砂石上。這個群組的社區佔據了從地下到相當的斜坡和山頂,具有各種方面和肥沃的土壤。分類的社區類型沿著地理、土壤濕度、土壤深度和面部相交的漸層分隔,大致可分為 " dry " 和 " 乾性 " 套裝。
Dry calcareous forests occur on subxeric to xeric, fertile habitats over carbonate formations of limestone and dolostone, or very rarely highly calcareous siltstone or shale. Habitats are steep, usually rocky, south- to west-facing slopes at elevations from < 300 to 900 m (< 1,000 to 2,900 ft). Soils vary from circumneutral to moderately alkaline and have high calcium levels. Confined in Virginia to the mountains, these communities are most frequent and extensive in the Ridge and Valley, but occur locally in both the Blue Ridge and Cumberland Mountains. Tree canopies vary from nearly closed to quite open and woodland-like. Overstory mixtures of chinquapin oak (Quercus muehlenbergii), sugar maple (Acer saccharum), black maple (Acer nigrum), northern red oak (Quercus rubra), white oak (Quercus alba), Shumard oak (Quercus shumardii), white ash (Fraxinus americana) and blue ash (Fraxinus quadrangulata, extreme southwest Virginia only) are typical. These forests and woodlands share many understory and herbaceous plants with the Piedmont / Mountain Basic Woodlands group and are similarly species-rich. A few of the taxa that are confined to or most important in the limestone and dolostone communities include Carolina buckthorn (Frangula caroliniana), round-leaved ragwort (Packera obovata), robin's-plantain (Erigeron pulchellus var. pulchellus), American beakgrain (Diarrhena americana), slender muhly (Muhlenbergia tenuiflora), black-seed ricegrass (Patis racemosa), limestone purple sedge (Carex purpurifera, in extreme southwestern Virginia only), hairy sunflower (Helianthus hirsutus), small-headed sunflower (Helianthus microcephalus), northern leatherflower (Clematis viorna), and white death-camas (Anticlea glauca). Logging and fire exclusion are probably the biggest threats to dry calcareous forests.

Dry-mesic calcareous forests occur in deeper soils of valley sideslopes, lower mountain slopes, gentle crests, and ravines up to about 1,150 m (3,800 ft) elevation. Forests of this group are widely distributed in the Ridge and Valley province, more local in the Cumberland Mountains, and rare in the northern Piedmont Triassic Basin. Mixtures of sugar maple (Acer saccharum), black maple (Acer nigrum) , chinquapin oak (Quercus muehlenbergii), white oak (Quercus alba), northern red oak (Quercus rubra), black oak (Quercus velutina), white ash (Fraxinus americana), and hickories (Carya spp.) are typical. A distinctive variant is co-dominated by eastern white-cedar (Thuja occidentalis), usually in association with eastern white pine (Pinus strobus), eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis), and hardwoods. Tulip-tree (Liriodendron tulipifera) is most abundant as an invader of logged stands. Understory and herbaceous vegetation varies from sparse to lush (especially on limestone sites), but is generally dominated by species characteristic of submesic soil moisture conditions, such as white snakeroot (Ageratina altissima var. altissima), hog-peanut (Amphicarpaea bracteata), common eastern bromegrass (Bromus pubescens), sharp-lobed hepatica (Hepatica acutiloba), and common black cohosh (Actaea racemosa).
乾性石灰岩森林可以很容易與豐富灣和斜坡森林或基本梅西森林的出現在受保護較低的地區,以及缺乏明顯的間生物植物,例如藍海豚(C aulophyllum thalictroides)、寬葉水葉(Hydrophyllum canadense)或木(Laportea canadensis)。許多乾燥的鈣質森林已經被嚴重切割或破壞,以便農業用途。在某些情況下,樹木似乎是由更多的間生物種(尤其是楓糖)入侵的橡木樹林,可能是長期排除火災的結果。白灰是一種非常常見的關聯樹木在乾燥和乾燥的鈣質森林中,目前正因祖母綠白灰山毛蟲爆發而出現顯著的死亡率。
參考文獻:弗萊明(1999),弗萊明和庫林(2001),弗萊明和穆爾黑德(1996),弗萊明和穆爾黑德(2000),拉溫斯基等。(1996)。 © DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
© DCR-DNH,加里 ·P· 弗萊明。
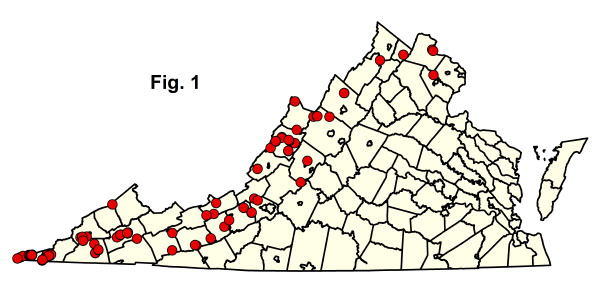
102 定量繪圖樣本支持七種社區類型(圖。1)。大多數單位的分類相當穩定,但只有從坎伯蘭山脈和南嶺和山谷知道的三種類型的完整分佈和狀態尚不清楚,需要額外清查。點擊下面的任何突出顯示的 CEGL 代碼以查看由 NatureReserve 瀏覽器提供的全球 USNVC 描述。
 下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。
下載下面列出的每種社群類型的組成摘要統計資料表。

